IIT Indore’s breakthrough Anti-TB Compounds show promise in tackling drug-resistant strains
1 min read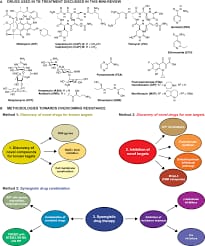
Indore(Team Newsbuddy) : India, which bears nearly half of the world’s tuberculosis (TB) burden, spends thousands of crores annually on subsidized anti-TB drugs. A significant advancement has been made at IIT Indore, where researchers have developed new compounds that could revolutionize TB treatment, potentially reducing long-term healthcare costs and bolstering indigenous drug development efforts.
These newly developed compounds have undergone extensive testing in bacterial cultures, demonstrating potent efficacy at low concentrations without harming immune cells like macrophages. Notably, they have successfully killed TB bacteria isolated from patients, including strains resistant to standard drugs like isoniazid, offering a promising solution to the growing challenge of multidrug-resistant (MDR) and extensively drug-resistant (XDR) TB.
Currently, the most effective of these compounds are being tested in small animal models, such as mice, with the aim of improving therapies for MDR and XDR-TB. The ultimate goal of this research is to provide new tools for treating TB, particularly drug-resistant forms, which remain a significant global challenge.
The innovative method used to develop these compounds has been granted patents in both India and the USA for treating various diseases, marking a significant step forward in the fight against TB and other infectious diseases





